Capsicum-genomics
https://ezcn.github.io/Capsicum-genomics/
The Capsicum collection
Capsicum is one of the major vegetable crops grown world-wide. This website contains information on an exciting project on the genetics of Capsicum.
Check the preprint on
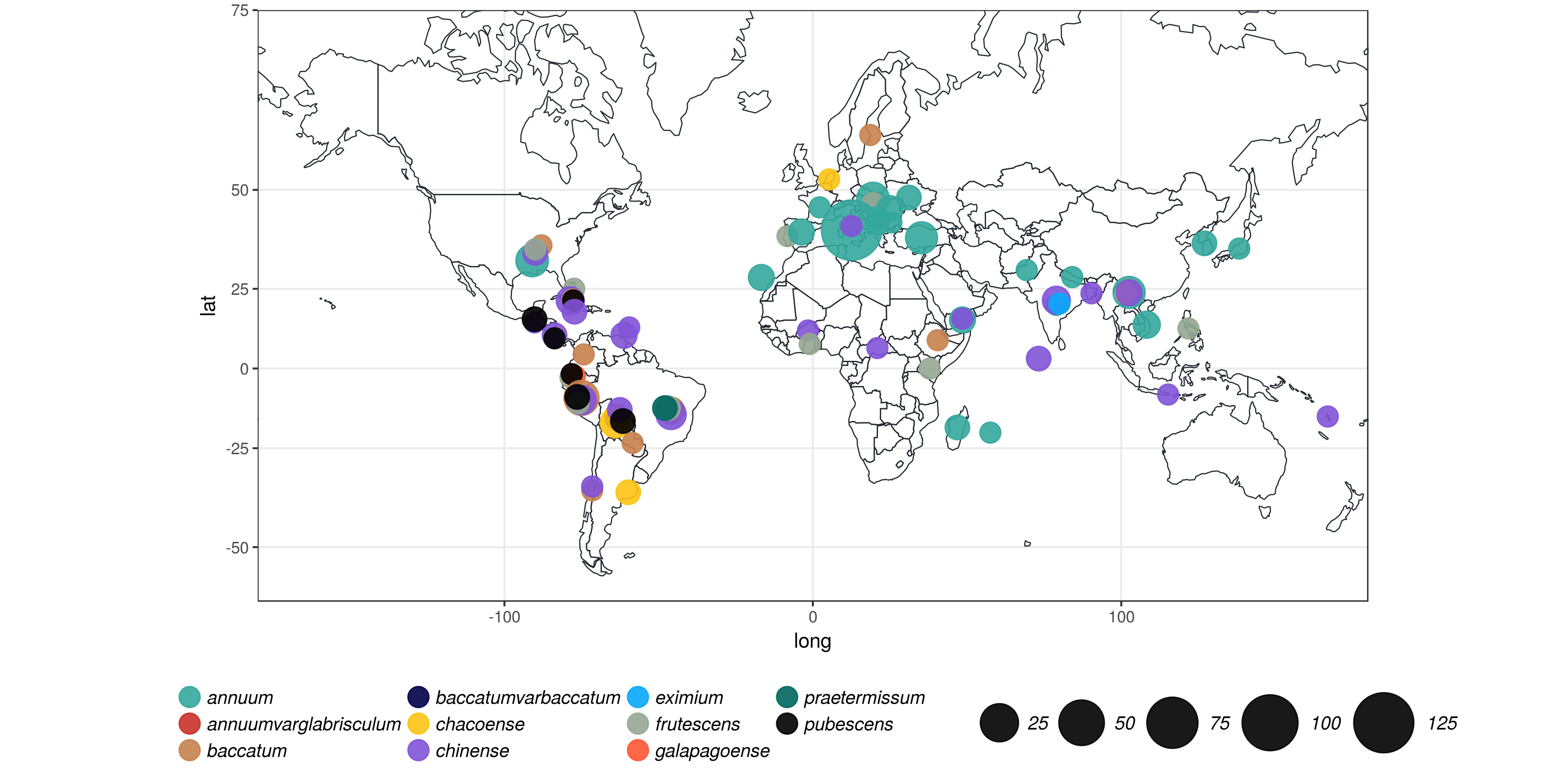
Samples Summary
| Species | # of diploid accessions | Type |
|---|---|---|
| C. annuum | 220 | domesticated |
| C. chinense | 62 | domesticated |
| C. baccatum (varpendulum) | 39 | domesticated |
| C. frutescens | 14 | domesticated |
| C. chacoense | 13 | wild |
| C.pubescens | 13 | domesticated |
| C. annuum var glabriusculum | 5 | wild |
| C. praetermissum | 3 | wild |
| C. baccatum var baccatum | 2 | domesticated |
| C. galapagoense | 1 | wild |
| C.eximium | 1 | wild |
Genomic diversity of the Capsicum genus at 746k variable sites.

We discovered 746k variable sites by sequencing 1.8% of the genome in a collection of 373 accessions belonging to 11 Capsicum species from 51 countries.
The majority of variants is single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), followed multi-nucleotide polymorphisms (MNP) and insertions/deletion (INDEL). A very small fraction of variants is complex combinations of SNP, MNP, and INDEL. QUAL>10 refers to Phred-scaled quality scores.
</br>
</br>
</br>
</br>
</br>
</br>
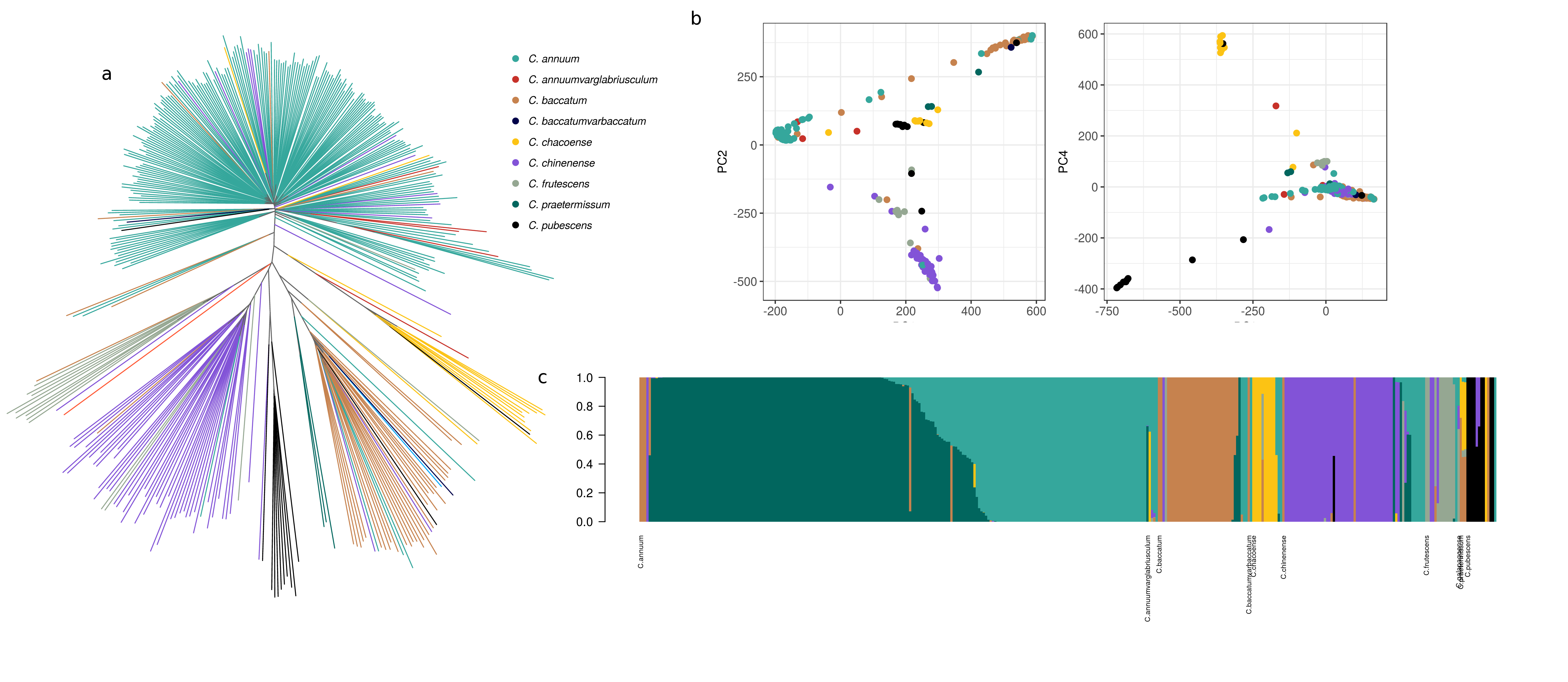
Population structure of Capsicum reveals strong subdivisions with little or no admixiture among species.
Population structure of the Capsicum species derived from 746k genome variants.
a)Phylogenetic reconstruction of the relationship between the accessions. With a few exceptions, clusters corrispond to species. b)Principal component analysis. The first two components separate the three main domesticated species. The third and the fourth components separate C. pubescens and C. chacoense between them and from the cluster of domesticated species. c)Model based admixture analysis in the hypothesis of seven clusters. With the exceptions of few admixed or misplaced individuals, clusters to corrispond to species and within C. annuum is possible to observe two groups with distinct genetic features.
Insight into C. annuum fruit variability from high resolution phenotyping.
Fruits broad variability has been driven by breeding programs and has been mainly studied by linkage analysis. We carried out phenotyping of the 220 accessions of C. annuum at thirty-eight phenotypic traits, in order to describe and understand the range of variation of C. annum fruits.
Graphic rapresentation of the phenotypes measured.
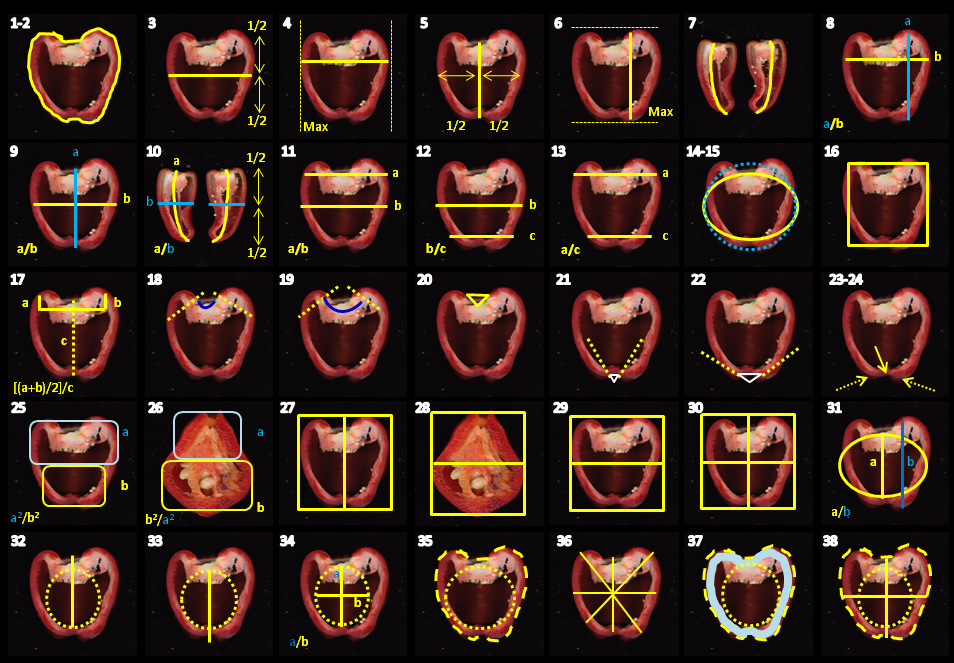
Bulky and large peppers are genetically different from small ones
Subdivision within C. annuum accessions into two clusters is associated with significant differences in four traits related to fruit size
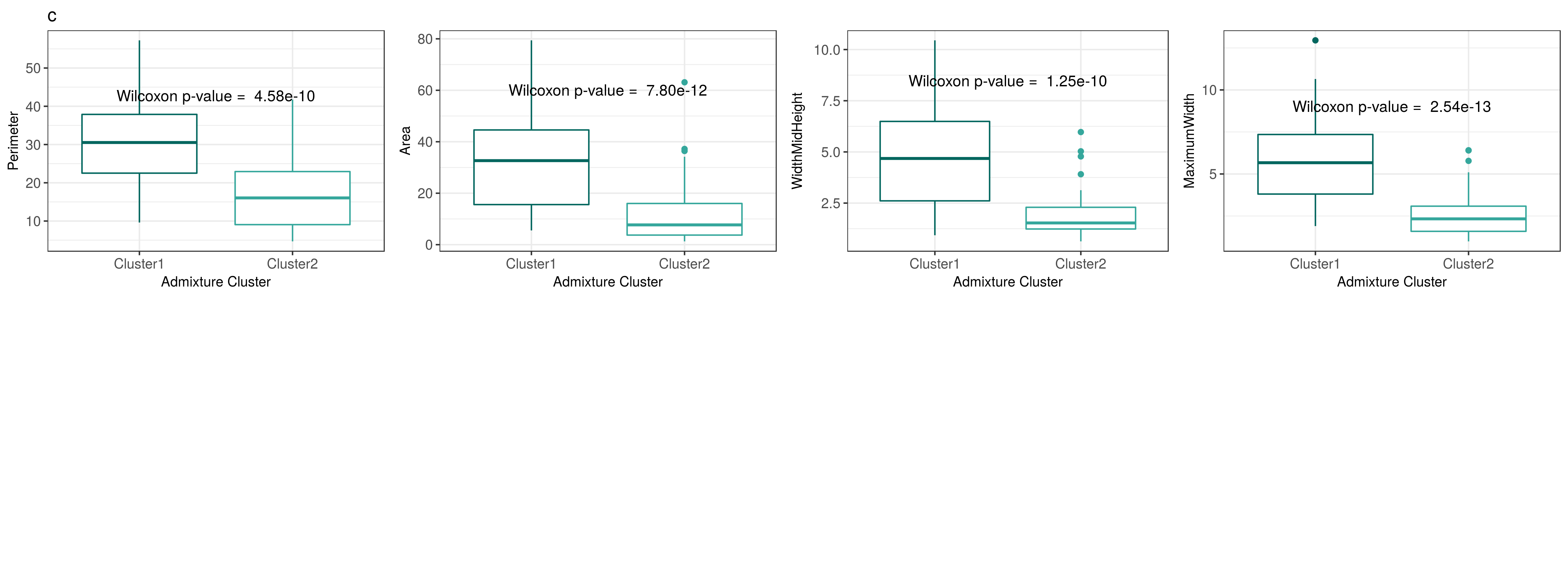
Accessions from C. annuum were assigned to genetic clusters determined in the admixture analysis if membership to the cluster was > 90%. Of the 38 traits, AREA, MAXIMUMWIDTH, WIDTHMIDHEIGHT, and PERIMETER are significantly different between the two genetic clusters. Fruit size is significantly different between the two genetic clusters, with Cluster 1 having bulkier and larger fruits relative to Cluster 2. This suggests that differences in fruit size in C. annuum might be caused by genetic differences.
Genetics of fruit in C. annuum.
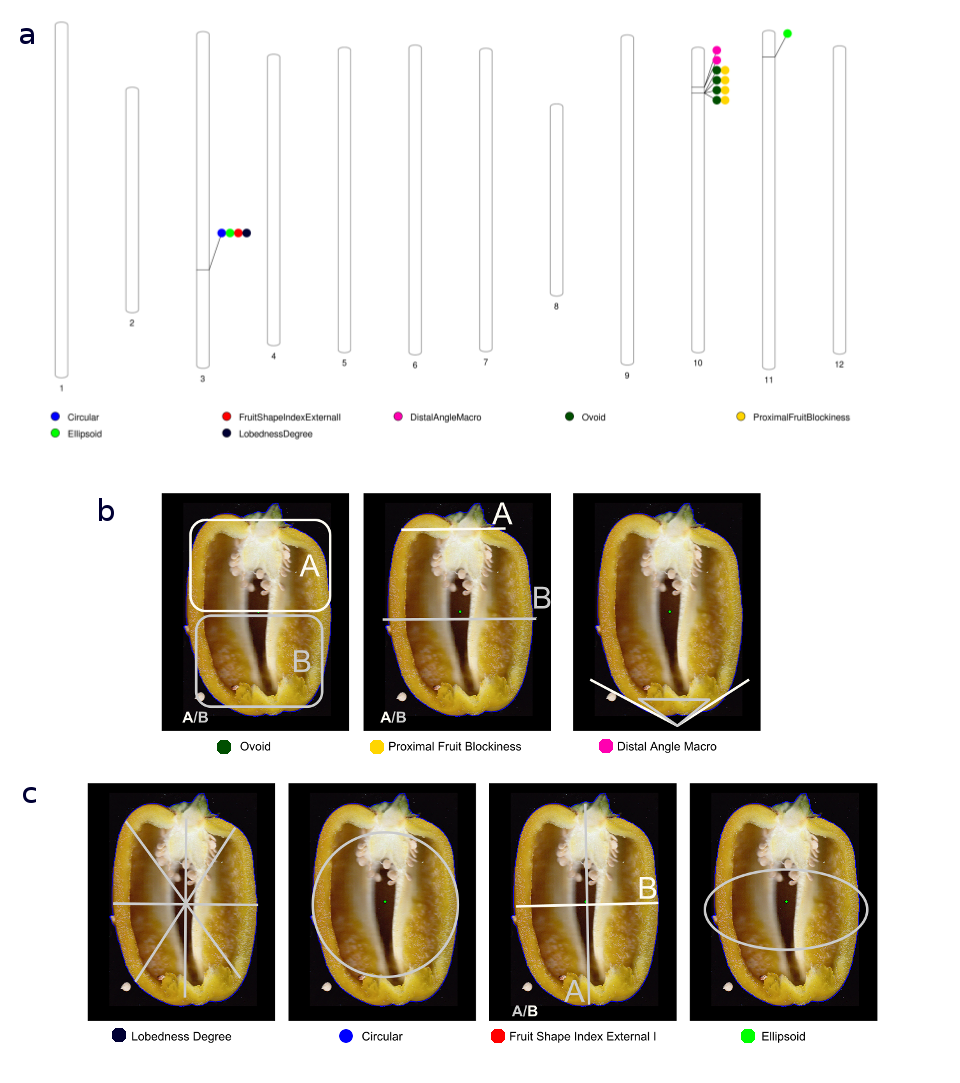
Results of the genome-wide association anlysis.
a)We identified eight variants at four loci on three chromosomes, significant associated with seven traits. Circles represent association between one genetic variant and one trait. Colors distingish phenotype. b)Cluster of phenotype determining whether fruits are pointed or squared. c)Cluster of phenotypes determining if fruits are circular or elongated.
Loci significantly associated with phenotypes related to fruit shape with genome-wide significance.
Min/Maj = minor and major alleles; MAF = Minor Allele Frequency; β = Coefficient describing the effect size of the marker in the univariate linear model of association; SE = Standard Error of β; p-value = genome-wide Bonferroni corrected p-value for association.
| Chr:position | Genomic region | Nearest gene (kb) | Min/Maj Alleles | MAF | Phenotype | β | SE | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3:183386147 | CA03g16080 | 0 | C/T | 0.13 | Circular | 0.10 | 0.016 | 1.36E-08 |
| Ellipsoid | 0.03 | 0.005 | 1.58E-10 | |||||
| Fruit Shape Index External I | 0.91 | 0.145 | 4.93E-09 | |||||
| Lobedness Degree | 16.97 | 2.449 | 1.38E-10 | |||||
| 10:28759675 | Intergenic | CA10g04730 (-911) | T/C | 0.36 | Distal Angle Macro | 18.47 | 2.962 | 4.97E-09 |
| 10:28759685 | Intergenic | CA10g0473 (-910) | T/G | 0.36 | Distal Angle Macro | 18.47 | 2.962 | 4.97E-09 |
| 10:33533810 | Intergenic | CA10g05040 (166) CA10g05050 (-156) | C/T | 0.22 | Ovoid | -0.08 | 0.012 | 8.87E-10 |
| Proximal Fruit Blockiness | -0.12 | 0.018 | 1.91E-10 | |||||
| 10:33533831 | Intergenic | CA10g05040 (167) CA10g05050 (156) | T/A | 0.22 | Ovoid | -0.08 | 0.012 | 8.87E-10 |
| Proximal Fruit Blockiness | -0.12 | 0.018 | 1.91E-10 | |||||
| 10:33534094 | Intergenic | CA10g05040 (169) CA10g05050 (-156) | T/A | 0.22 | Ovoid | -0.08 | 0.012 | 8.87E-10 |
| Proximal fruit Blockiness | -0.12 | 0.018 | 1.91E-10 | |||||
| 10:33557960 | Intergenic | CA10g05040 (408) CA10g05050 (-132) | C/G | 0.1 | Ovoid | -0.15 | 0.024 | 5.43E-09 |
| Proximal fruit Blockiness | -0.24 | 0.036 | 4.04E-10 | |||||
| 11:18204293 | Intergenic | CA11g04570 (849) CA11g04580 (-892) | T/A | 0.06 | Ellipsoid | 0.04 | 0.006 | 4.39E-09 |
A non-synonymous change in the Longifolia 1-like gene is associated with variance in C. annuum fruit elongation
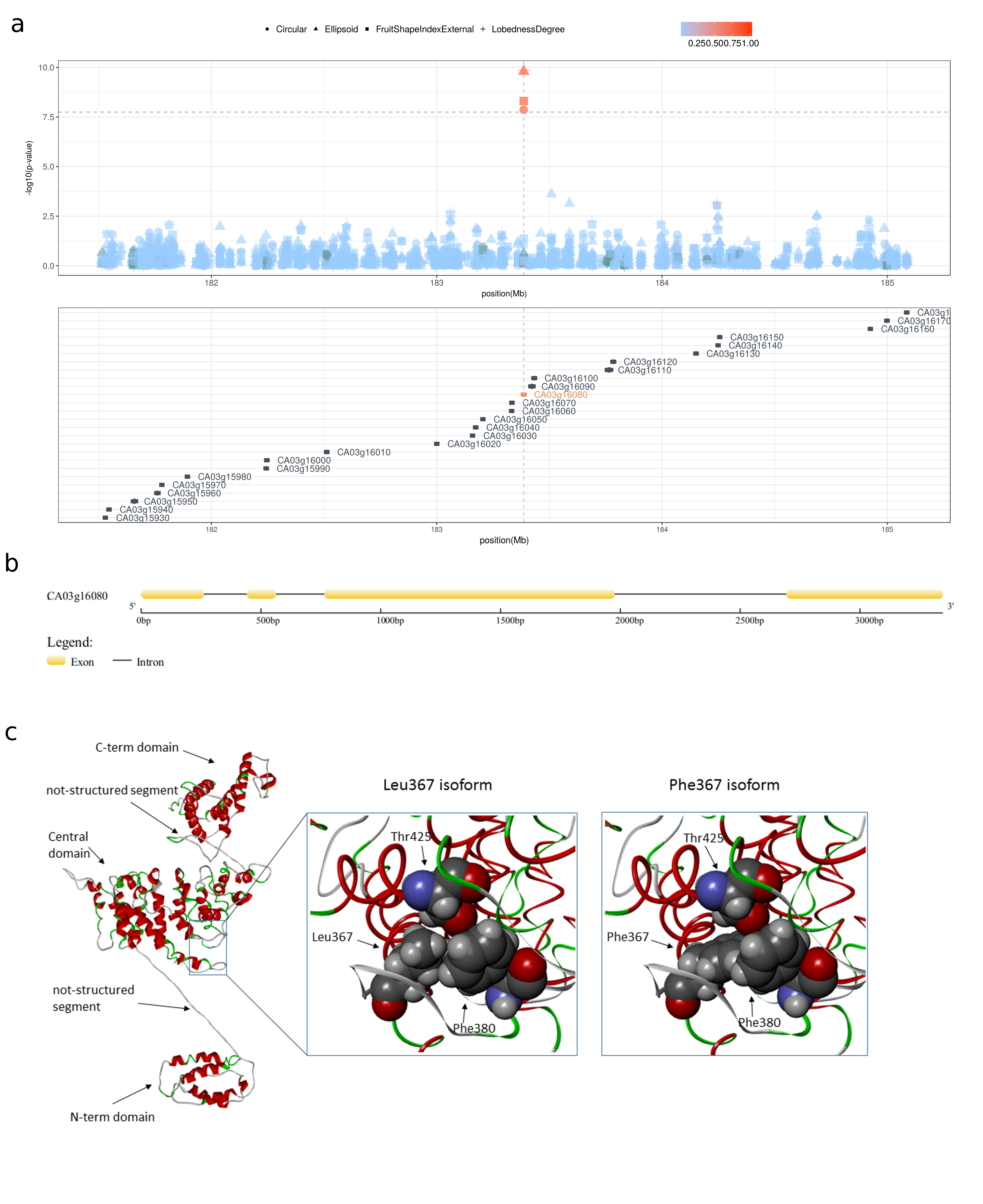
The Longifolia 1-like gene region.
a)Locus zoom plot in a region of ±2Mb surrounding the non-synonymous mutation (3:183386147) in the gene Longifolia 1-like (CA03g16080) showing that the 3:183386147 variant is the only one reaching a genome-wide significant thereshold for genetic association in a region containing twenty-six genes. Color gradient indicate linkage desequilibrium mesuared ad r². b)The predict genic structure of Langifolia 1-like (CA03g16080). c)Predict protein structure for Langifolia 1-like.
Allele frequencies at the single nucleotide polymorphism 3:18338614 in Capsicum species.
Numbers in parentheses indicate haploid sample size.
| Species (n) | CTC (Leu) | TTC (Phe) |
|---|---|---|
| C. annuum (412) | 0.23 | 0.76 |
| C. frutescens (28) | 0.02 | 0.98 |
| C. chinense (90) | 0.03 | 0.97 |
| C. baccatum (72) | 0 | 1 |
| C. chacoense (26) | 0 | 1 |
| C. pubescens (26) | 0 | 1 |